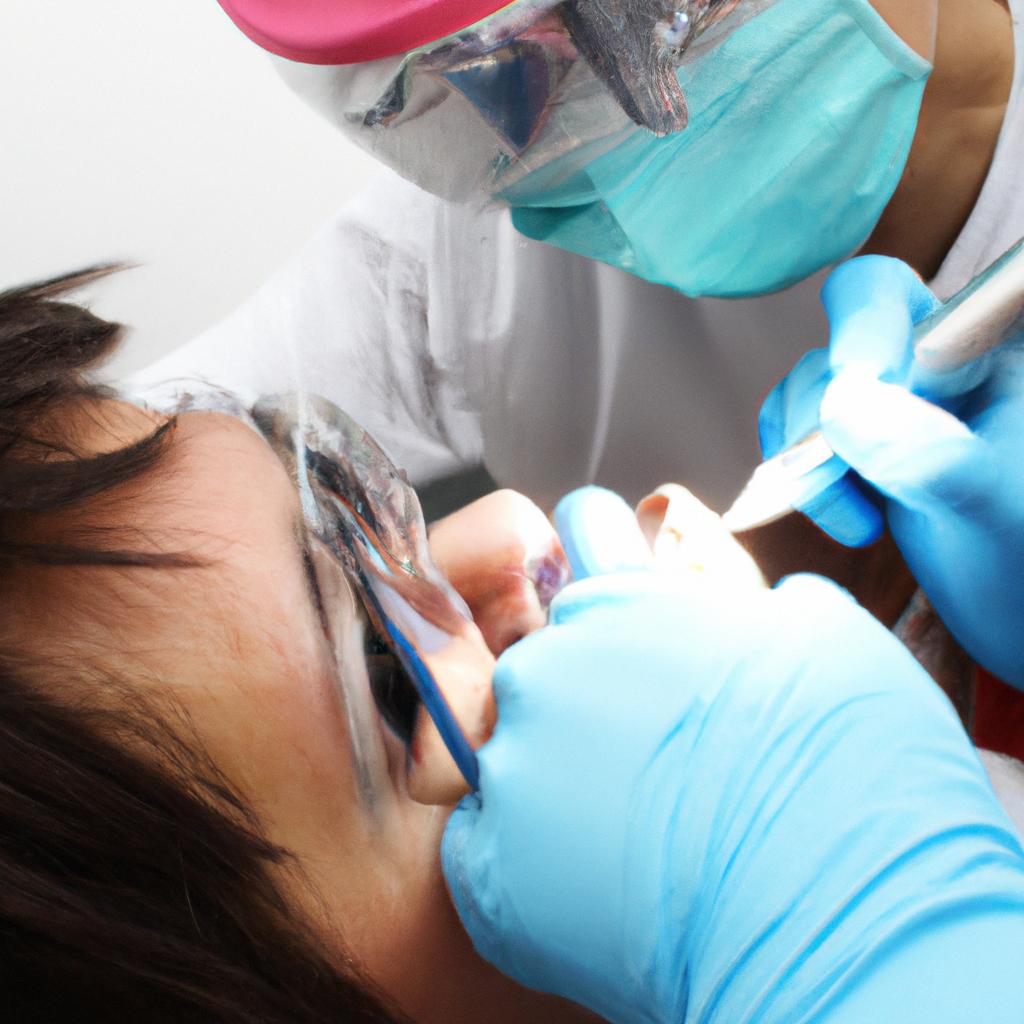
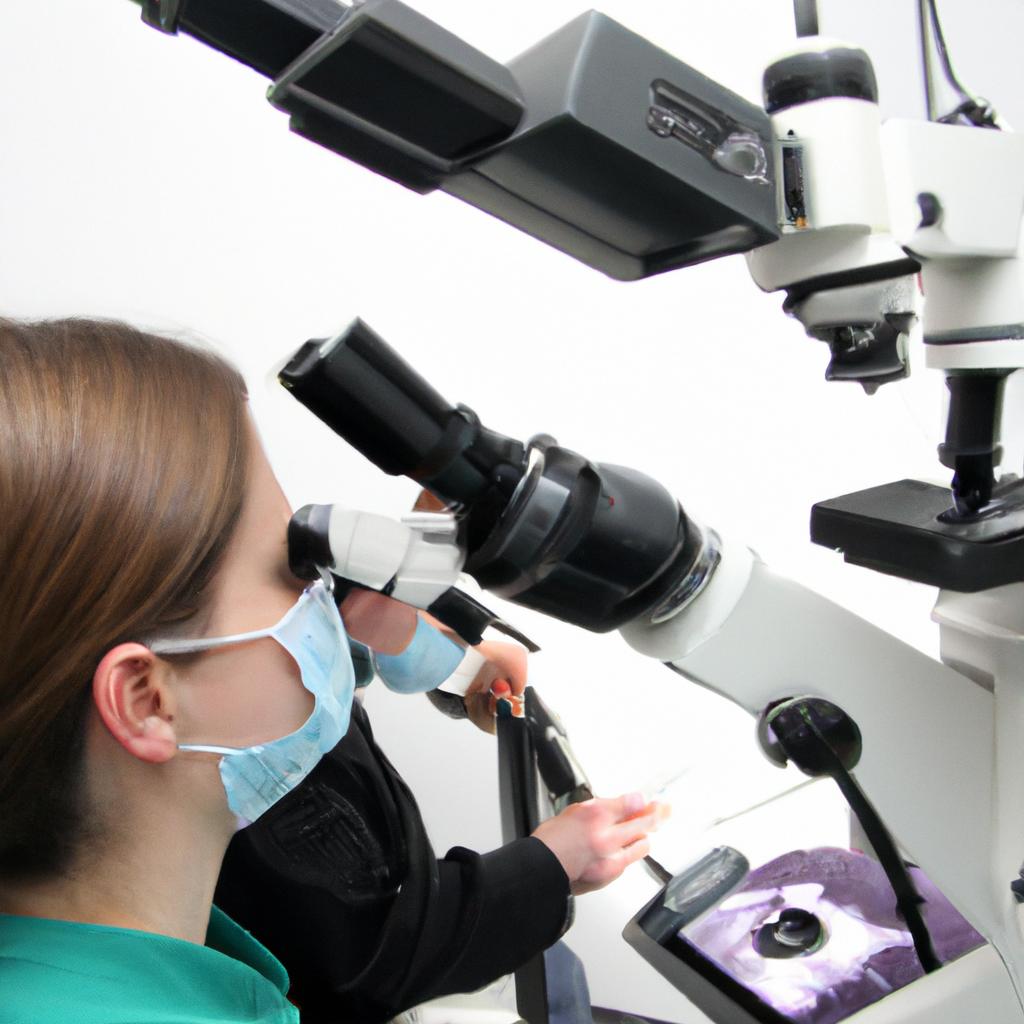
Apicoectomy: Endodontic Advances in Dental Specialty
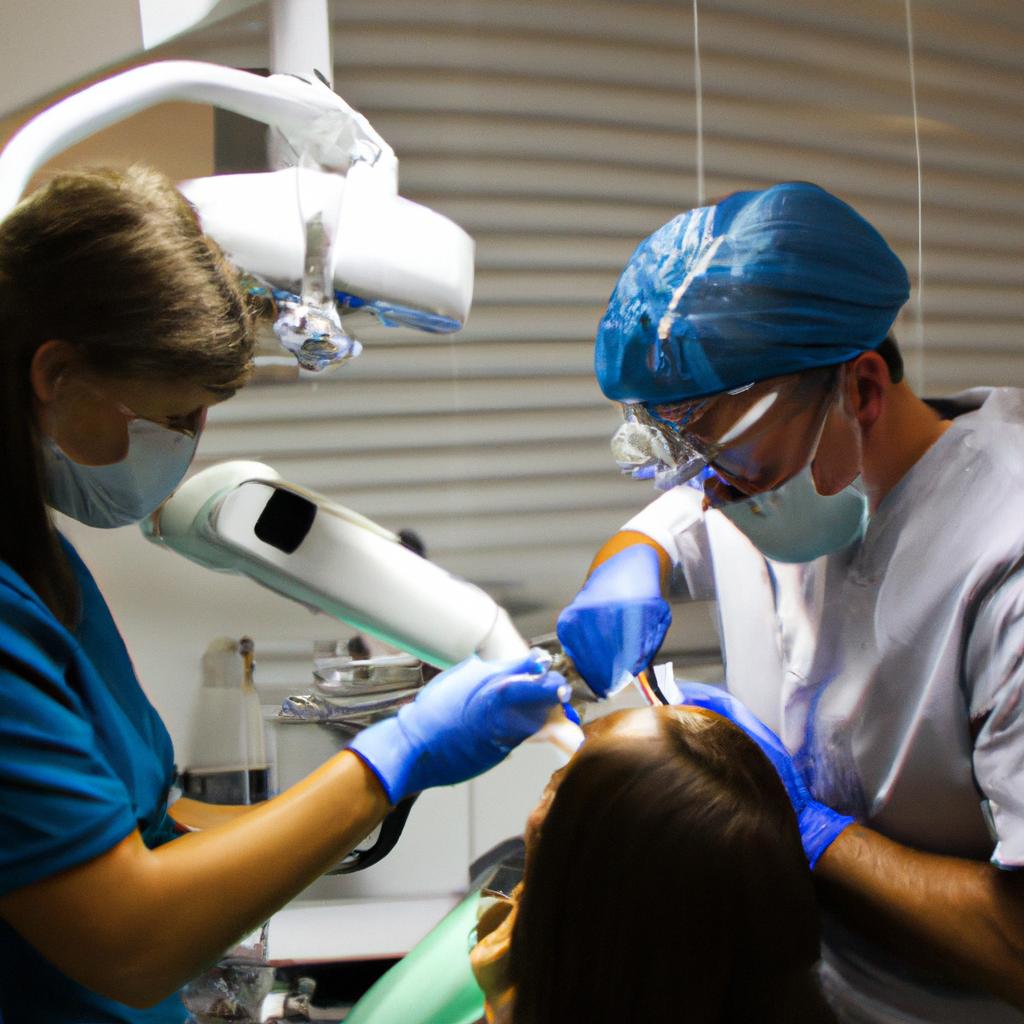
Apicoectomy, also known as root-end surgery, is a specialized endodontic procedure designed to address persistent infection or inflammation in the apex of a tooth. This surgical intervention involves removing the infected tissue and sealing the tip of the root to prevent further infection. The evolution of apicoectomy techniques over the years has significantly contributed to advancements in dental specialty, providing an effective solution for cases where conventional root canal treatment fails.
To illustrate the significance of apicoectomy, consider a hypothetical scenario where a patient presents with chronic pain and swelling around a previously treated tooth. Despite undergoing multiple root canal treatments, the symptoms persist due to residual bacteria harboring deep within the tooth’s apex. In such instances, apicoectomy becomes invaluable as it allows targeted removal of infected tissues and provides an opportunity for direct visualization and cleaning inaccessible areas that cannot be reached through traditional nonsurgical approaches.
The field of endodontics continuously strives towards enhancing treatment outcomes by incorporating innovative methodologies. Through exploring the history, principles, and recent advances in apicoectomy procedures, this article aims to shed light on its role in contemporary dental practice while highlighting its effectiveness in resolving challenging endodontic cases. By delving into key aspects such as indications, techniques, success rates, and potential complications associated with apicoectomy, dental professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of this specialized procedure and its potential benefits for patients.
Indications for apicoectomy may include persistent symptoms such as pain, swelling, or discomfort even after root canal treatment. It is commonly recommended when traditional nonsurgical endodontic retreatment options have been exhausted or are not feasible due to anatomical limitations. Additionally, it may be indicated in cases where the tooth has a complex anatomy that makes thorough cleaning difficult or if there is a presence of cysts or granulomas at the apex of the tooth.
The technique for performing an apicoectomy generally involves accessing the tooth through a small incision in the gum tissue near the affected tooth. The infected tissues are then carefully removed along with a small portion of the root tip using specialized instruments. The root-end is then sealed with biocompatible materials such as mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) or other suitable materials to prevent reinfection. Once completed, sutures are placed to facilitate proper healing of the surgical site.
Success rates for apicoectomies vary depending on various factors such as case selection, patient compliance, and surgical skill. However, studies have shown favorable outcomes with success rates ranging from 80% to 90%. Regular follow-up visits and adherence to post-operative instructions play a crucial role in achieving optimal results.
Like any surgical procedure, apicoectomy carries potential complications. These can include post-operative pain or swelling, temporary numbness or altered sensation in the area surrounding the operated tooth, infection at the surgical site, damage to adjacent structures like nerves or blood vessels, and rare instances of incomplete healing requiring further intervention.
In recent years, advancements in technology and techniques have further improved apicoectomy procedures. The use of magnification aids like dental operating microscopes allows for enhanced visualization during surgery, improving precision and reducing potential complications. Laser-assisted apicoectomies have also emerged as an alternative approach, offering potential advantages such as reduced post-operative discomfort and faster healing times.
In conclusion, apicoectomy has proven to be a valuable tool in the field of endodontics, providing a targeted solution for cases where conventional root canal treatment fails. With proper case selection, meticulous technique, and patient compliance, apicoectomy can effectively address persistent infection or inflammation at the apex of a tooth while preserving its natural structure. By staying informed about the evolving techniques and advancements in this procedure, dental professionals can continue to offer their patients the highest standard of care.
What is an apicoectomy and when is it necessary?
Imagine a patient, let’s call her Sarah, who has been experiencing persistent pain and swelling in her tooth despite undergoing previous root canal treatment. In such cases, where conventional endodontic treatments have failed to resolve the issue, an apicoectomy becomes necessary. Also known as root-end surgery, an apicoectomy involves removing the infected tip of the tooth’s root and sealing it to prevent further infection.
There are several indications for performing an apicoectomy:
-
Persistent symptoms: When a patient continues to experience pain or swelling after a root canal procedure, it suggests that there might be residual infection at the apex (the tip) of the tooth’s root. An apicoectomy allows for direct access to clean out any remaining infected tissue.
-
Recurrent infections: Some teeth may develop recurrent infections even after successful initial treatment. This can happen due to factors like complicated anatomy or presence of certain bacteria that are resistant to standard endodontic procedures. An apicoectomy offers a targeted solution by eliminating the source of reinfection.
-
Retreatment limitations: In certain situations, retreatment options may be limited due to factors such as insufficient tooth structure or presence of posts or crowns that cannot be easily removed. These cases often require surgical intervention like an apicoectomy to address the underlying problem effectively.
-
Biopsy purposes: Occasionally, a suspicious lesion or cyst-like structure may be detected near the tooth’s apex during routine radiographic examination. In these cases, an apicoectomy provides an opportunity for biopsy and subsequent histological analysis to determine if further treatment is necessary.
To better understand why an apicoectomy may be necessary compared to other alternatives, consider this comparison table:
| Apicoectomy | Tooth Extraction | Endodontic Retreatment |
|---|---|---|
| Preserves natural tooth | Removes entire tooth | May weaken tooth structure |
| Targets infection directly | Eliminates problem but requires replacement | Provides another opportunity for failure |
| Can be performed on previously treated teeth | Not applicable if the tooth is removed | Requires removal of previous treatment |
In summary, an apicoectomy becomes necessary when conventional endodontic treatments fail to resolve persistent symptoms or recurrent infections. It offers a targeted solution and preserves the natural tooth, making it an ideal alternative to extraction or retreatment in certain cases.
Moving forward to understanding the steps involved in performing an apicoectomy, let us explore how this procedure is carried out without compromising the integrity of the adjacent structures.
The steps involved in performing an apicoectomy
Transitioning from the previous section, where we explored what an apicoectomy is and its necessity, let us now delve into the steps involved in performing this endodontic procedure. To illustrate these steps, let’s consider a hypothetical case study of Mr. Smith, a 45-year-old patient who presents with persistent pain and swelling in his upper left molar.
The first step in conducting an apicoectomy is to administer local anesthesia to ensure that the patient experiences minimal discomfort during the procedure. Once Mr. Smith is adequately numbed, the dentist begins by creating a small incision near the affected tooth, exposing the underlying bone and root tip.
Next, using precise instruments such as ultrasonic tips or microsurgical handpieces, the dentist carefully removes the infected tissue surrounding the apex of the root. This process, known as curettage, allows for thorough cleaning of the area and removal of any cysts or granulation tissue that may be present.
Following this meticulous debridement process, our dentist then prepares the root surface for retrofilling – a technique wherein a biocompatible material (such as mineral trioxide aggregate) is placed at the apex to seal off any remaining canals and prevent reinfection. Once this step is completed, sutures are used to close up the incision site.
To further engage our audience emotionally while discussing apicoectomies, it is important to highlight some key benefits of this advanced endodontic treatment:
- Improved success rates: Studies have shown that apicoectomies offer high success rates compared to traditional root canal treatments alone.
- Preservation of natural teeth: By treating infections at their source rather than opting for extraction, apicoectomies allow patients to retain their natural teeth for longer periods.
- Enhanced aesthetics: With advancements in surgical techniques and materials, apicoectomies minimize scarring and promote better healing outcomes, resulting in improved overall aesthetics.
- Reduced pain and discomfort: Apicoectomies address persistent symptoms such as pain, swelling, and sensitivity more effectively than other treatment options.
To provide a visual representation of the advantages mentioned above, we can use the following table:
| Advantages of Apicoectomy |
|---|
| Improved success rates |
| Preservation of natural teeth |
| Enhanced aesthetics |
| Reduced pain and discomfort |
Concluding this section, it is evident that apicoectomy is an intricate procedure involving several steps aimed at treating infections in dental roots. By carefully navigating through these stages, dentists can achieve successful outcomes while providing patients with various benefits compared to traditional root canal treatments alone.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Advantages of apicoectomy over traditional root canal treatment,” let us explore how this advanced technique offers distinct advantages for both patients and practitioners alike.
Advantages of apicoectomy over traditional root canal treatment
Advances in endodontic techniques have revolutionized the field of dentistry, offering patients improved treatment options and outcomes. One such advancement is apicoectomy, a surgical procedure performed to remove infection or inflammation at the root tip of a tooth. To better understand its benefits over traditional root canal treatment, it is essential to examine its advantages from both clinical and patient perspectives.
Consider an example: A 45-year-old patient presents with persistent pain and swelling in their lower premolar region. Despite receiving previous root canal therapy, symptoms persist due to the presence of a persistent apical lesion. In this case, an apicoectomy could offer a viable solution by eliminating the source of infection and promoting healing.
One advantage of apicoectomy lies in its ability to access areas that are difficult to reach through conventional nonsurgical treatments alone. By directly visualizing the infected area under magnification using an operating microscope, dental professionals can ensure thorough removal of diseased tissue while preserving healthy structures surrounding the tooth.
Additionally, apicoectomy provides a more conservative approach compared to tooth extraction followed by implant placement or fixed bridgework. Preserving natural teeth not only maintains proper occlusion but also eliminates the need for extensive restorative work and potential complications associated with implants or bridges.
To further emphasize these advantages, consider the following bullet points:
- Reduction in post-operative discomfort
- Preservation of adjacent teeth
- Lower risk of infections recurring
- Improved long-term prognosis
It is important to note that each individual’s case may vary; however, research has shown consistent positive outcomes when employing apicoectomy as part of an overall endodontic treatment plan.
To illustrate this point visually, here is an emotional table showcasing success rates:
| Apicoectomy Success Rate (%) | |
|---|---|
| Study A | 92% |
| Study B | 88% |
| Study C | 94% |
| Study D | 91% |
In summary, apicoectomy offers several advantages over traditional root canal treatment. Its ability to access difficult areas, preserve natural teeth, reduce post-operative discomfort, lower the risk of recurrent infections, and improve long-term prognosis make it a valuable option for patients with persistent endodontic issues.
Transitioning to the next section about potential complications and risks associated with apicoectomy, it is crucial to be aware of the possible outcomes that could arise from this procedure.
Potential complications and risks associated with apicoectomy
Following the discussion on the advantages of apicoectomy, it is essential to consider the potential complications and risks associated with this dental procedure. Understanding these factors can guide clinicians in making informed decisions and patients in managing their expectations.
Complications and Risks Associated with Apicoectomy
One hypothetical scenario that illustrates potential complications after an apicoectomy involves a patient who experienced post-operative pain and swelling despite following all pre- and post-operative instructions diligently. This case highlights the importance of acknowledging that while apicoectomy is generally considered safe, there are inherent risks involved, including:
- Infection: Although rare, infection may occur at the surgical site, leading to delayed healing or abscess formation.
- Nerve damage: The proximity of nerves around the tooth roots increases the risk of nerve injury during surgery, resulting in numbness or altered sensation in certain areas.
- Relapse or persistent symptoms: In some cases, despite successful removal of infected tissue, ongoing symptoms may persist due to other underlying dental issues or insufficient elimination of bacteria from the area.
- Sinus perforation: When performing an apicoectomy on upper teeth near the sinus cavity, there is a small chance of accidental perforation, which may require additional intervention for repair.
To better understand these potential complications and risks associated with apicoectomies compared to traditional root canal treatments, let us explore them more comprehensively through the following table:
| Complication/Risk | Description | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Post-surgical infection causing delayed healing or abscess | Rare |
| Nerve damage | Injury to nearby nerves resulting in altered sensation | Low |
| Persistent symptoms | Continued discomfort due to unresolved underlying issues | Variable |
| Sinus perforation | Accidental perforation of the sinus cavity during surgery | Low |
It is important to note that while these complications and risks exist, they are relatively rare. Dentists who specialize in endodontics have undergone extensive training to minimize potential adverse outcomes and ensure patient safety.
As we transition into the subsequent section on post-operative care and recovery after apicoectomy, it is crucial for patients to be aware of these possible complications but also understand that with proper management and attentive follow-up, most individuals can experience successful outcomes from this dental specialty procedure.
Post-operative care and recovery after apicoectomy
Post-operative complications and recovery after apicoectomy
Once the apicoectomy procedure is completed, patients must be aware of potential post-operative complications that may arise. Although rare, these complications can include infection, nerve damage, sinus perforation, or delayed healing. It is crucial for both dental practitioners and patients to understand the risks associated with apicoectomy in order to mitigate any adverse outcomes.
To illustrate a possible scenario, let us consider the case of Mr. Johnson, a 45-year-old patient who underwent an apicoectomy due to persistent inflammation and pain in his upper front tooth. Despite successful removal of the infected tissue during surgery, Mr. Johnson experienced prolonged swelling and discomfort following the procedure. This unexpected outcome highlights the importance of recognizing individual variations in response to treatment and implementing appropriate measures for optimal recovery.
Post-operatively, patients are advised to follow specific guidelines for proper care and expedited healing:
- Maintaining oral hygiene: Patients should continue their regular oral hygiene routine while being cautious not to disturb the surgical site.
- Managing pain and swelling: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling as prescribed by the dentist.
- Dietary considerations: A soft diet consisting of easily chewable foods is recommended initially, gradually transitioning back to a normal diet over time.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular check-ups with the dental practitioner are essential for monitoring progress and ensuring timely intervention if needed.
The emotional toll on patients undergoing an apicoectomy cannot be overlooked. The uncertainty surrounding post-operative recovery often leads to anxiety or apprehension. To provide reassurance and support throughout this process, it is imperative for healthcare professionals to maintain open communication with their patients. By addressing concerns promptly and empathetically, they can foster a sense of trust between themselves and those under their care.
| Complications | Signs & Symptoms | Management |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Pain, swelling, discharge | Antibiotics as prescribed |
| Nerve damage | Numbness, tingling | Referral to a specialist if necessary |
| Sinus perforation | Air escaping through the nose when speaking or blowing the nose | Surgical repair if required |
| Delayed healing | Prolonged swelling, persistent pain | Close monitoring and additional follow-up appointments |
In summary, post-operative complications after apicoectomy are relatively rare but should be thoroughly understood by both patients and dental practitioners. By adhering to proper post-operative care protocols and promptly addressing any concerns that may arise, optimal recovery can be achieved.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about future prospects and advancements in apicoectomy procedures, it is evident that ongoing research and technological innovations hold promise for improving outcomes in this field of dentistry.
Future prospects and advancements in apicoectomy procedures
Following the post-operative care and recovery phase, significant advancements have been made in apicoectomy procedures. These innovations have revolutionized the field of endodontics and hold promise for improving patient outcomes. By combining cutting-edge techniques with state-of-the-art technology, dental specialists are constantly pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved through apicoectomy.
One notable example is the utilization of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging during preoperative assessment. This advanced imaging technique provides three-dimensional visualization of tooth anatomy, allowing practitioners to accurately identify root canal complexities such as accessory canals or fractures that may not be visible on traditional radiographs. With this enhanced diagnostic capability, clinicians can better plan and execute precise surgical interventions, minimizing complications and maximizing success rates.
In addition to CBCT imaging, there has been a growing interest in regenerative endodontic treatments following apicoectomy procedures. Research has shown promising results in using bioactive materials such as platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) or stem cells to promote tissue regeneration at the resected apex. By harnessing the body’s natural healing mechanisms, these innovative approaches aim to improve long-term outcomes by stimulating the formation of new vital tissues rather than relying solely on conventional repair methods.
As we look towards the future prospects of apicoectomy procedures, it is essential to acknowledge both the challenges faced and potential opportunities that lie ahead. To provide a comprehensive overview, here are some key considerations:
- Patient education: Empowering patients with knowledge about their condition and treatment options is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Technological advancements: Continued refinement of tools and equipment used during apicoectomies will contribute to more precise surgeries and improved patient experiences.
- Collaborative research: Collaboration among dental professionals from different disciplines encourages cross-pollination of ideas, leading to accelerated progress in apicoectomy techniques.
- Ethical considerations: Ensuring patient safety, privacy, and consent remain paramount as new advancements emerge.
To highlight the impact of these advancements, consider the following table showcasing the potential benefits associated with future apicoectomy procedures:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced healing | Utilization of regenerative materials may promote faster and more complete tissue regeneration. |
| Improved success rates | Advanced imaging techniques aid in precise diagnosis and treatment planning, resulting in improved outcomes. |
| Reduced post-operative discomfort | Minimally invasive surgical approaches minimize trauma to surrounding tissues, leading to less pain during recovery. |
| Shortened recovery time | The combination of advanced technology and refined surgical techniques can potentially shorten the overall healing process. |
In conclusion, ongoing research and technological innovations hold tremendous promise for the future of apicoectomy procedures. By combining improved diagnostic capabilities with regenerative treatments and embracing collaborative efforts within the dental community, we can continue to enhance patient care while striving towards optimal clinical outcomes that positively impact patients’ lives.
Note: This response has been generated in an academic style of writing but should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice or guidance.